Let’s be honest, keyword research can sound intimidating. But if you run an ecommerce store, it’s one of the most powerful ways to get your products in front of people who are actually searching for them.
The best part? Once you understand how it works, it’s not as complicated as it seems.
So what exactly is ecommerce keyword research?
It’s the process of figuring out which words and phrases your ideal customers are typing into Google when they’re looking for products like yours.
By understanding and targeting these search terms, you can optimize your website to rank higher, attract more visitors, and ultimately increase sales.
By conducting thorough keyword research, you can optimize your website’s content and structure to improve its visibility and attract more organic traffic, which can ultimately translate into more ecommerce sales.
Every time someone types something into Google, they’re telling you what they want. Good keyword research helps you show up with the right product at the right time, no guesswork needed!
However, performing ecommerce keyword research correctly is no easy feat. This is why it’s essential to understand the process of ecommerce keyword research thoroughly and use the best available tools to make informed decisions.
With the right set of keyword research tools and techniques, you can gain valuable insights into your target audience’s search behavior, identify relevant and high-performing keywords, and create an effective SEO strategy that drives results.
So, whether you’re just starting with SEO or looking to refine your existing strategy, investing time and effort into keyword research is vital for ecommerce success.
But here’s the catch, the way Google understands keywords has changed a lot over the years.
If you’re still thinking about SEO the way it worked in 2010, it’s time for a quick reality check.
How does Google process keywords today?
Back in the old days, SEO was a very straightforward process. All you needed to do to rank well was to find the right keywords, to insert them within your page content, and to add some backlinks.
The search results, however, were far from perfect. Keyword-stuffed websites received higher ranking than quality content providers – and that sucked.
That’s why in the past years Google has made several big changes to its algorithm, to enable it to better rank quality and relevant content, and punish SEO spammers.
In plain English? Google is getting really good at figuring out what people mean, not just what they type.
That means we, as ecommerce store owners or marketers, have to think a little deeper when choosing keywords. It’s not just about the exact words, it’s about the intent behind them.
Today, the search landscape is shifting thanks to powerful AI models known as LLMs, or Large Language Models. These are the same kinds of models behind tools like ChatGPT and Google’s new Search Generative Experience (SGE). They help search engines understand questions more deeply, summarize information, and even generate full answers right in the search results.
For ecommerce keyword research, this means you’re not just trying to rank for traditional links. You’re also aiming to appear in AI-generated summaries and featured responses.
The more clearly your content answers real customer questions, the better your chances of showing up.
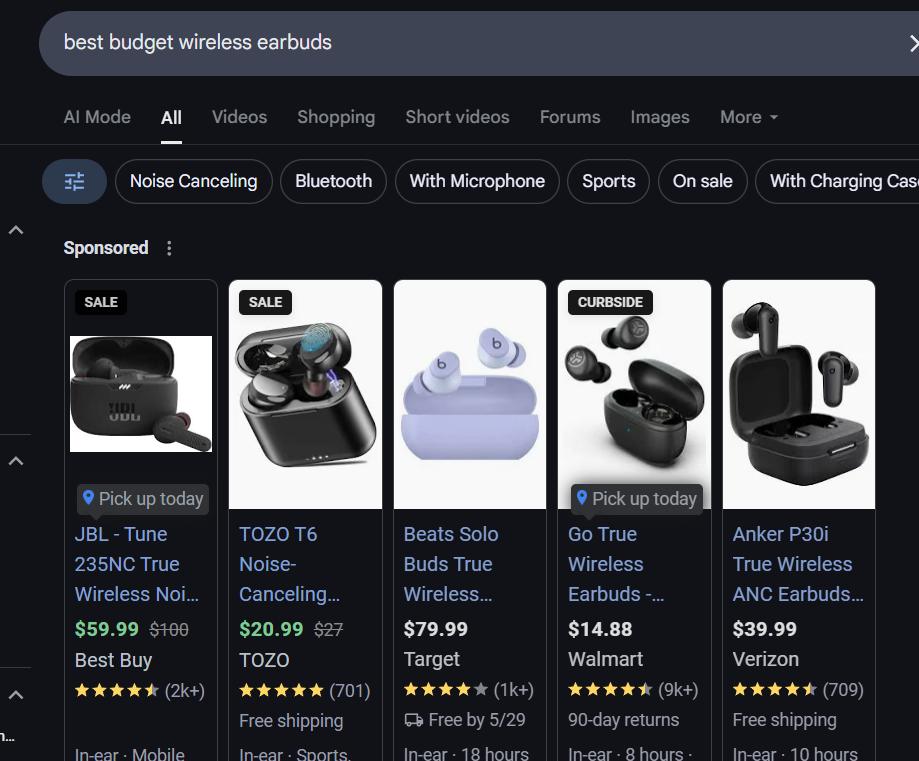
Let’s say someone types “best budget wireless earbuds” into Google. The searcher isn’t just typing random keywords — they’re clearly looking for affordable earbuds and likely getting ready to make a purchase.
Google understands this intent and shows a mix of comparison posts, product listings, and reviews. It’s not just about matching the exact phrase. It’s about understanding what the user wants and delivering the most helpful content.
That’s why, when you do ecommerce keyword research, you need to look beyond exact phrases. Think about the related terms your audience might use, the questions they’re asking, and how to naturally weave those into your content.
This means that when you’re performing your keyword research, you should think about which words are related to your main keywords, and how to use them in your content. To do that you must understand the different types of keywords according to SEO.
Types of Ecommerce Keywords (and Why They Matter)
Not all keywords are created equal. Some get tons of searches but almost never convert. Others might have low volume but bring in buyers who are ready to click “Add to Cart” right now. Understanding the different types of keywords will help you focus on the ones that actually grow your business, not just your traffic.
Search-engine marketers most often divide keywords into three main categories depending on their length and the difficulty of ranking for them.
- Head: These are most often one-word keywords with large amounts of search volume and insane competition. They are also not very specific, and as such they don’t convert as well. These are words like “notebook”, “watch”, “t-shirt”, etc. They don’t express if the user wants to find out products from that category, or just the meaning of the word.
- Body: These are two- or three-word phrases that get decent search volume (2,000+ searches per month). They almost always have lower competition, and are more specific than head words. Some great examples of such words are “summer vacation offers”, “notebook promotions”, and “shipping services”. You can see how they express the intent behind the search better.
- Long-tail keywords: These are really specific phrases, usually composed of four or more words. Single long-tail keywords typically have fewer searches per month; but if you combine them, you’ll be able to rank for the majority of the searches in your niche. These are words like “Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon Ultrabook”; “Where to buy books online” and “Flights from San Francisco to Buenos Aires”.
Your main goal with keyword research should be to find as many long-tail and body keywords as you can, as they are easier to rank for and have higher buying intent. This is how to begin.
How to Do Ecommerce Keyword Research (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Get Inside Your Customer’s Head
Every great ecommerce keyword strategy starts with one thing — understanding your customers. Before you even open up a keyword tool, take a step back and ask: What are my ideal buyers searching for? What do they care about? What words do they use?
The best way to start is by creating buyer personas and mapping out your customer journey and listening to how your customers talk. This means checking your support tickets, listening to sales calls, reading product reviews (yours and competitors’), and browsing social media comments.
Extracting keyword ideas directly from your clients: To do this effectively, you need to listen to and observe your target customers. What are the words they’re using when they’re talking about your brand, company or products?
The most effective ways to find this out are to:
- Conduct interviews or run surveys.
- Check out recorded sales and customer-support calls.
- Read customer-support emails.
- Read product reviews on yours and your competitors’ sites.
- Read posts and comments on your brand’s social media channels.
This part is easy to overlook, but it’s critical. These natural phrases from your customers can help you discover long-tail keywords and hidden search intent you won’t find in keyword tools.
After you’re done with extracting keyword ideas from your customers and ready for the next stage, separate them into groups. Each group must represent a different perspective and angle on the products and services that you’re offering.
Step 2: Think about how keywords are related to each other
Once you’ve gathered a list of phrases from customer research, start organizing them. Keywords that are closely related should be grouped together.
This will help you map out content ideas later , like product pages, blog posts, and even FAQ sections.
Once you have extracted keywords from your customers, think about how they are related to each other.
Put them into different groups, and brainstorm about other words you could include.
Google rewards sites that show deep topical authority. When your content uses related terms and covers a topic from multiple angles, you’re more likely to rank, not just for one keyword, but for dozens of variations.
Read this post to learn more about How to use mind mapping to organize keywords.
To better understand related keywords, look at this example:
Say I am running an e-commerce store that sells Air Jordan basketball shoes. I can start with the main phrase “Air Jordan”. I can then step into their shoes and start brainstorming other words/phrases they might search for, such as:
- Nike Jordans for kids
- Are Air Jordans good for basketball?
- Michael Jordan shoes collection
- J’s sneaker resale value
These aren’t just variations, they reflect different search intents. One user is looking to buy, another wants to compare, and another is researching history or value. Understanding that helps you create better-targeted content.
Remember, you will only come up with great new keyword ideas if you put in the time to get to know your customer.
Prioritize Your Keywords
Once you have your initial list of keywords, it’s important to prioritize them based on their potential impact on your business. One way to do this is by using a framework called the “Keyword Effectiveness Index” (KEI).
The KEI is a metric that helps you determine which keywords are worth targeting based on their search volume and competition level. To calculate the KEI for a keyword, you simply divide the keyword’s search volume by its competition level.
Here’s the formula:
KEI = (Monthly Search Volume)^2 / Competition
The higher the KEI, the more valuable the keyword is for your SEO strategy. Ideally, you want to target keywords with a high search volume and low competition, as these keywords have the potential to drive a significant amount of traffic to your website.
To prioritize your keywords using the KEI, simply calculate the KEI for each keyword on your list and sort them in descending order. Focus on targeting the keywords with the highest KEI first, as these are the keywords that are most likely to have a positive impact on your business.
It’s important to note that the KEI should not be the only factor you consider when prioritizing your keywords. You should also take into account factors such as relevance, user intent, and business goals when deciding which keywords to target.
Step 3: Use Keyword Tools to Discover What People Actually Search
Once you’ve done your homework on customers and grouped related terms, it’s time to dig deeper with keyword tools.
This is where you’ll uncover search volume, find long-tail gems, and expand your keyword list with data, not just guesses.
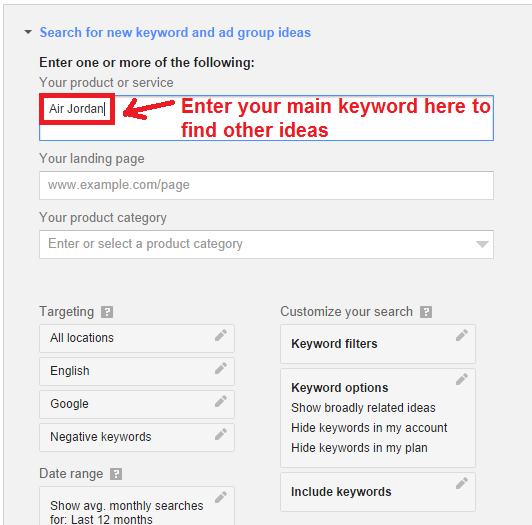
Find keywords with Google Keyword Planner: Login to your AdWords account, then go to Tools and Settings> Keyword Planner.
Click on “Keyword ideas”. Type in your desired keyword. For this example, we’re going to use Air Jordan.
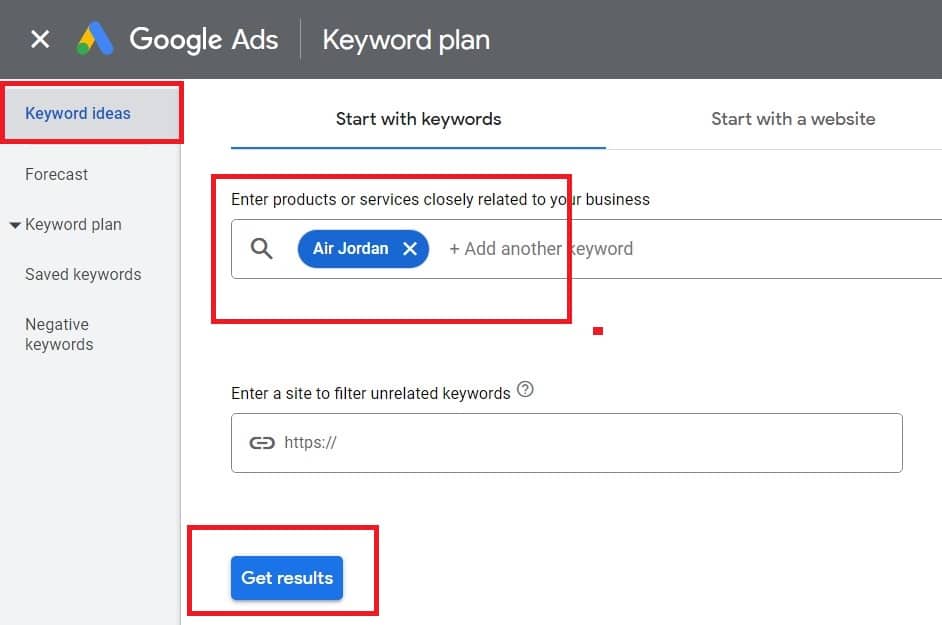

Click on “Get results” to see a result list of keyword ideas.
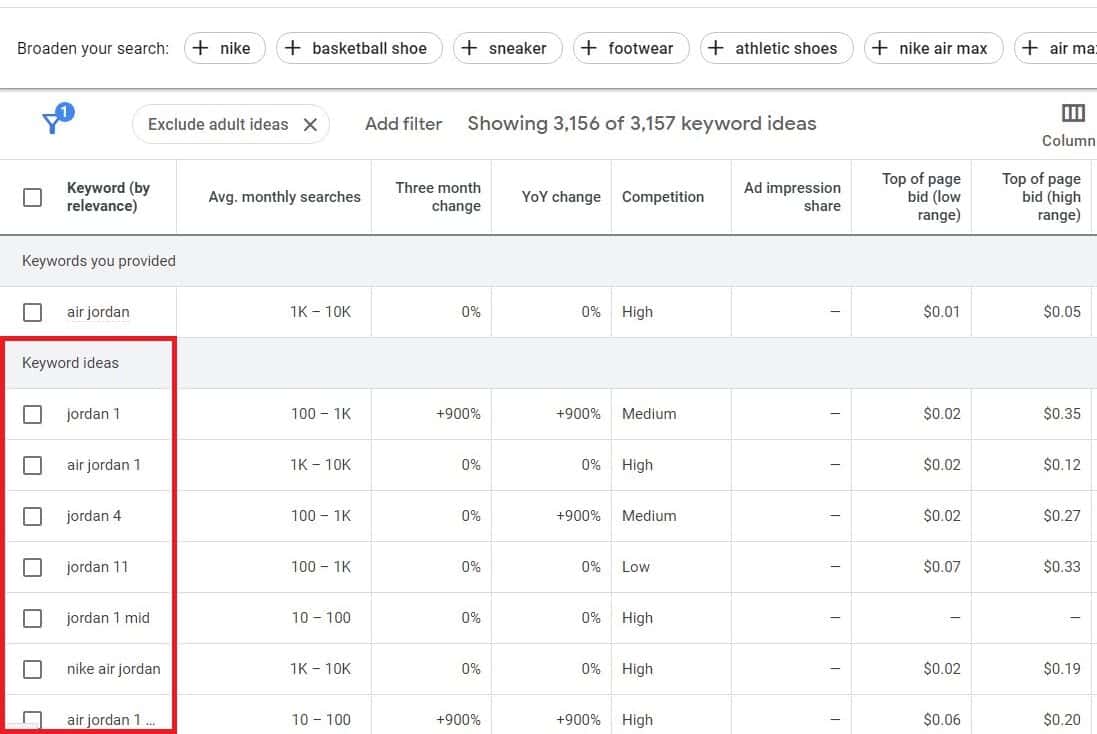
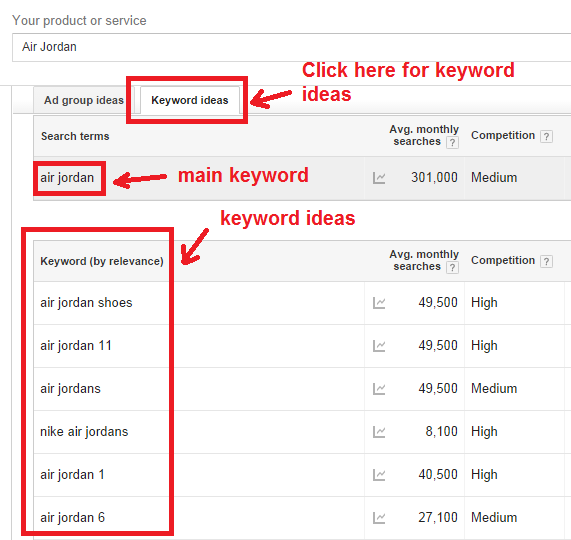

Try to find some long-tail keywords with lots of search volume, such as “Nike Air Jordan”.
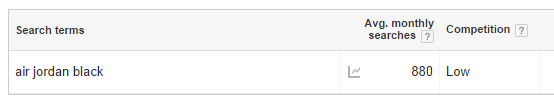

Find keywords with Google Autocomplete: Start typing keywords into Google, and you’ll see that the search engine will give you suggestions for completing your search. This is a great way to generate new keyword ideas.
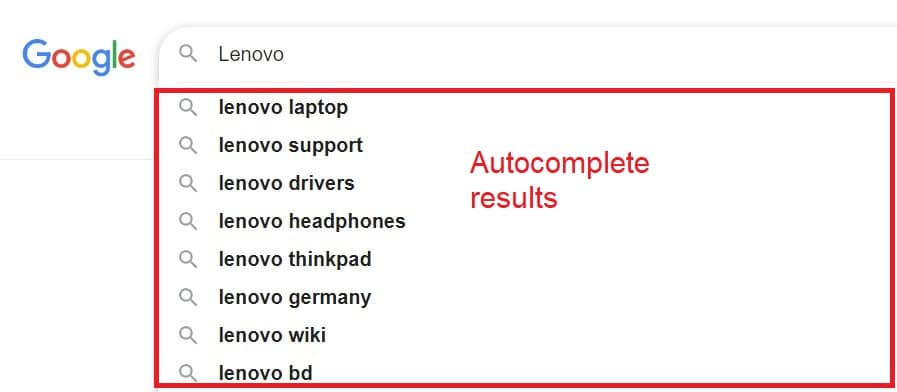
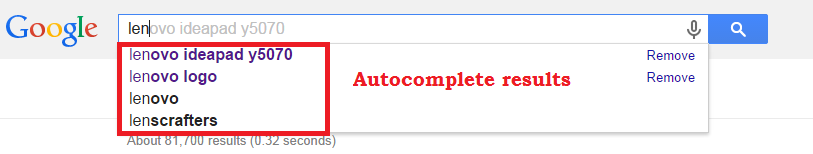

Find keywords with UberSuggest: This tool uses the power of Google Autocomplete without the need to type the words manually.
These are the suggestions that we get for “Lenovo”.
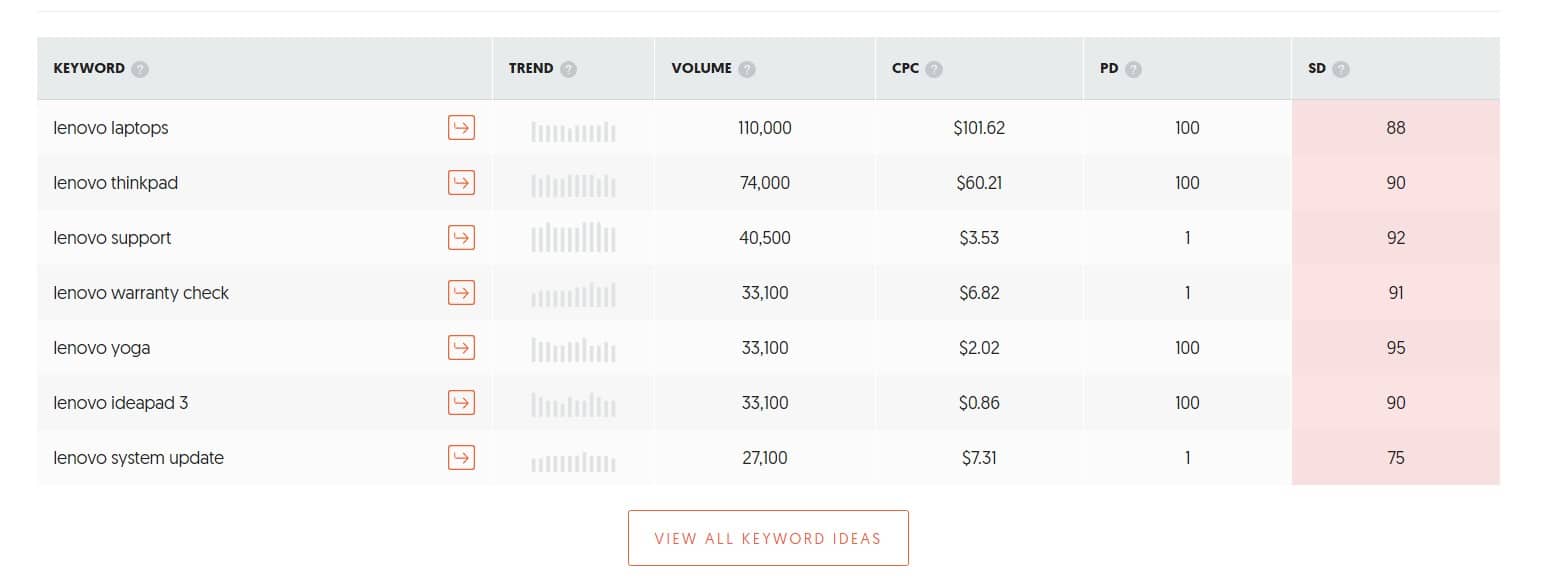


Find keywords with Site Search: Optimize for the keywords that your visitors are already using on your own website’s search engine to find products or services that you offer.
To find them, simply go to Google Analytics > Behavior > Site Search

You’ll then see the keywords you want to rank for in search engines.
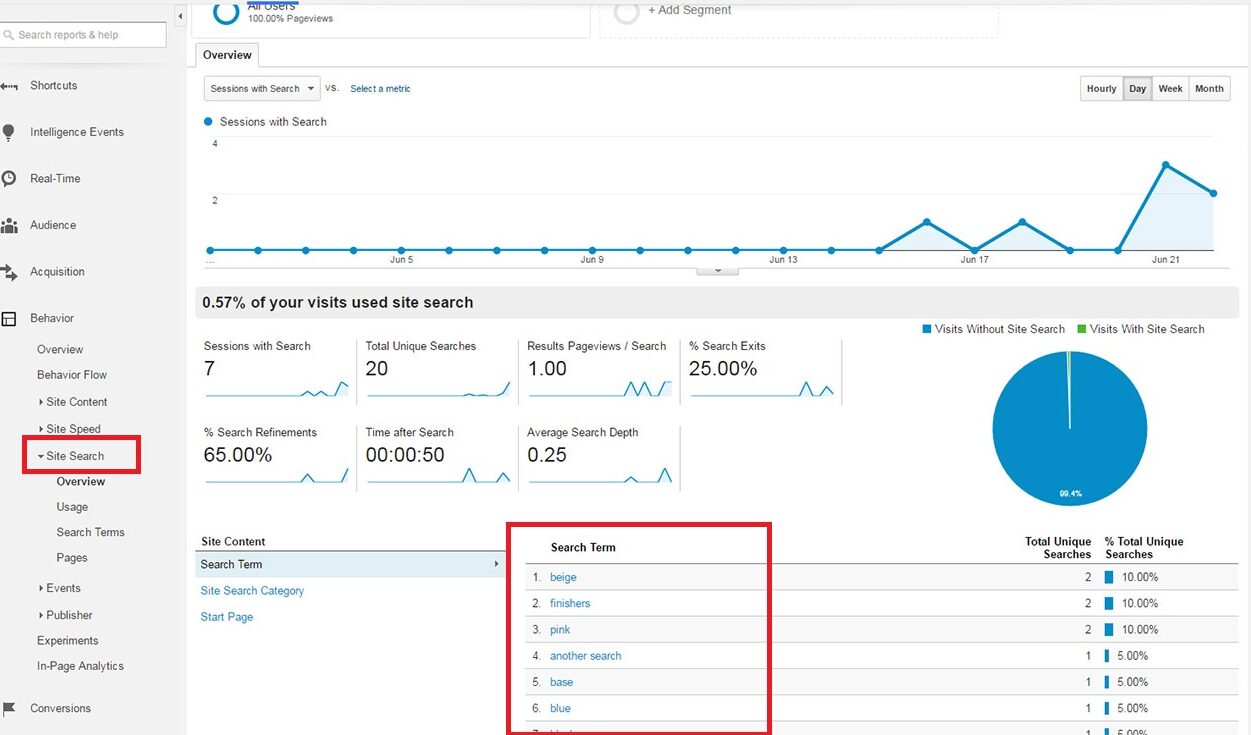
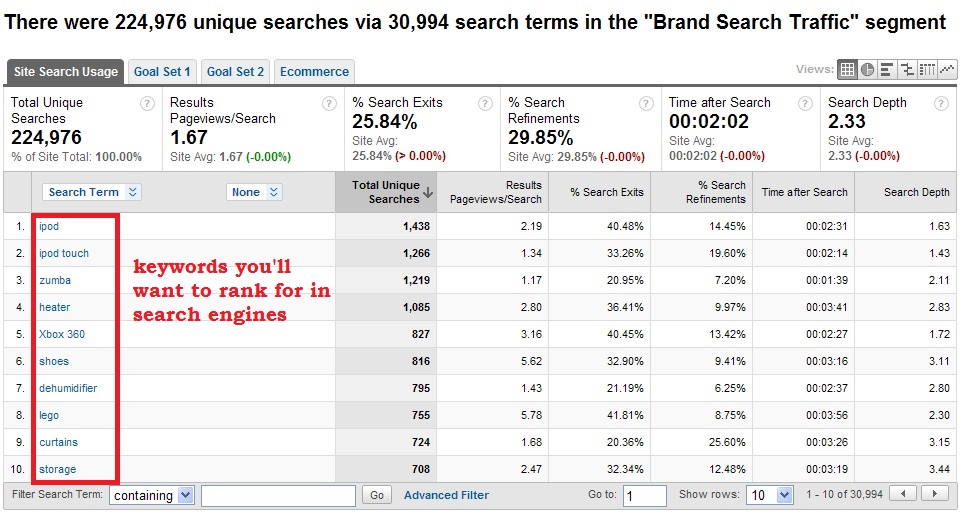

Check them out to see which ones are worth ranking for by reviewing their average monthly search volume and competition in Google Keyword Planner.
Find keywords with Google Search Console: Sometimes your site will be getting organic traffic from keywords that you don’t even know exist. You might not be ranking on the first page, but you’re still getting traffic. If these keywords are worthwhile, it makes sense to optimize for them – you just need to find them first. This is how you do it.
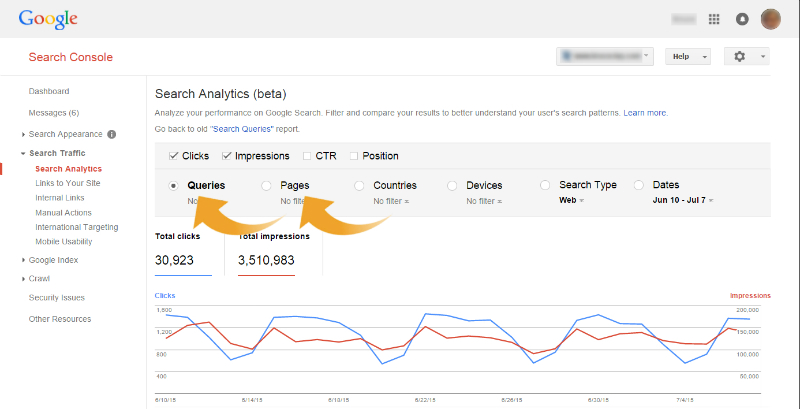
Go to Google Search Console -> Search traffic – > Search analytics

Then you’re going to see all the keywords your eCommerce site ranks for, including the number of impressions and clicks that you get.
Find keywords on Wikipedia: The largest free encyclopedia is a great resource tool for finding new keyword ideas. Here’s why:
- It is one of the best ranking websites on the Internet (for almost all keywords).
- You can find information on the site about almost anything you want.
This means that if you check out a page about a brand or product that you’re offering on your eCommerce site, you’ll probably get tons of keyword ideas.
Here’s what we find when we visit the page of Air Jordan:
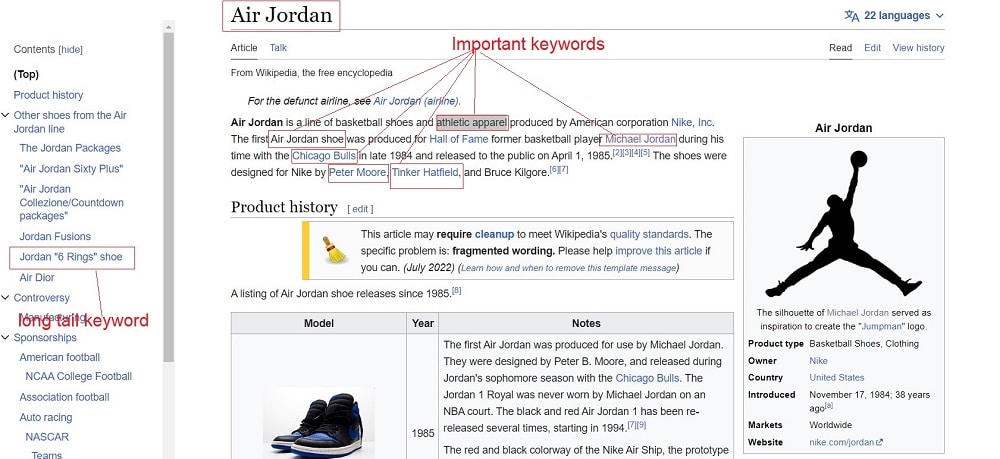
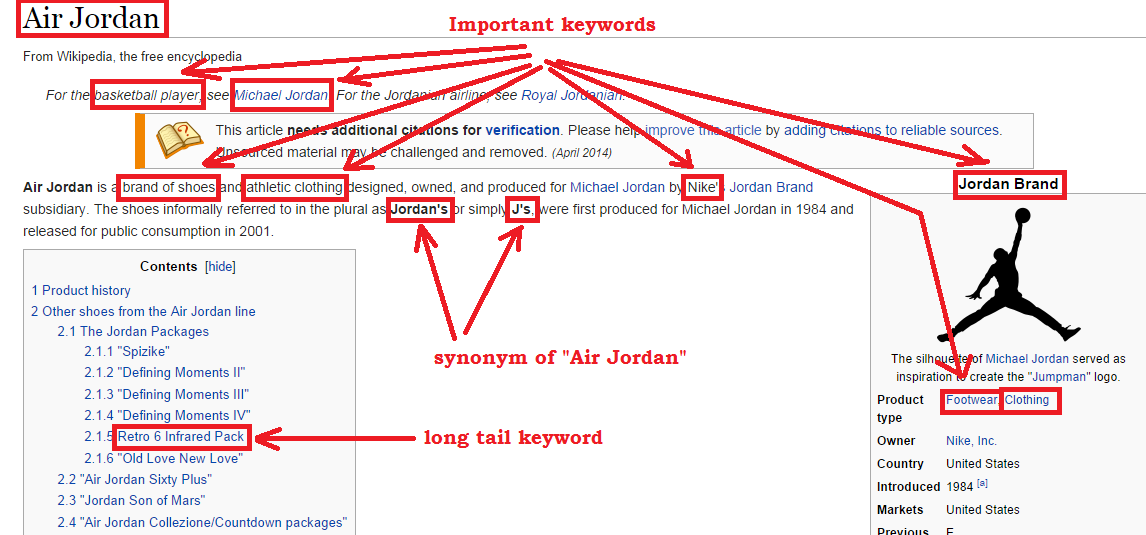

We find keywords like: “Michael Jordan”, “basketball player”, “Jordan’s , “Nike”, “Footwear”, “Clothing”, “Athletic clothing”, etc.
Find keywords on Amazon: the king of eCommerce ranks well for almost every product being sold online. Take advantage of this by learning which keywords they are using.
For example, if you’re selling GoPro Digital Action Camera. Go to Amazon and find the product page. This is where to search for keywords:
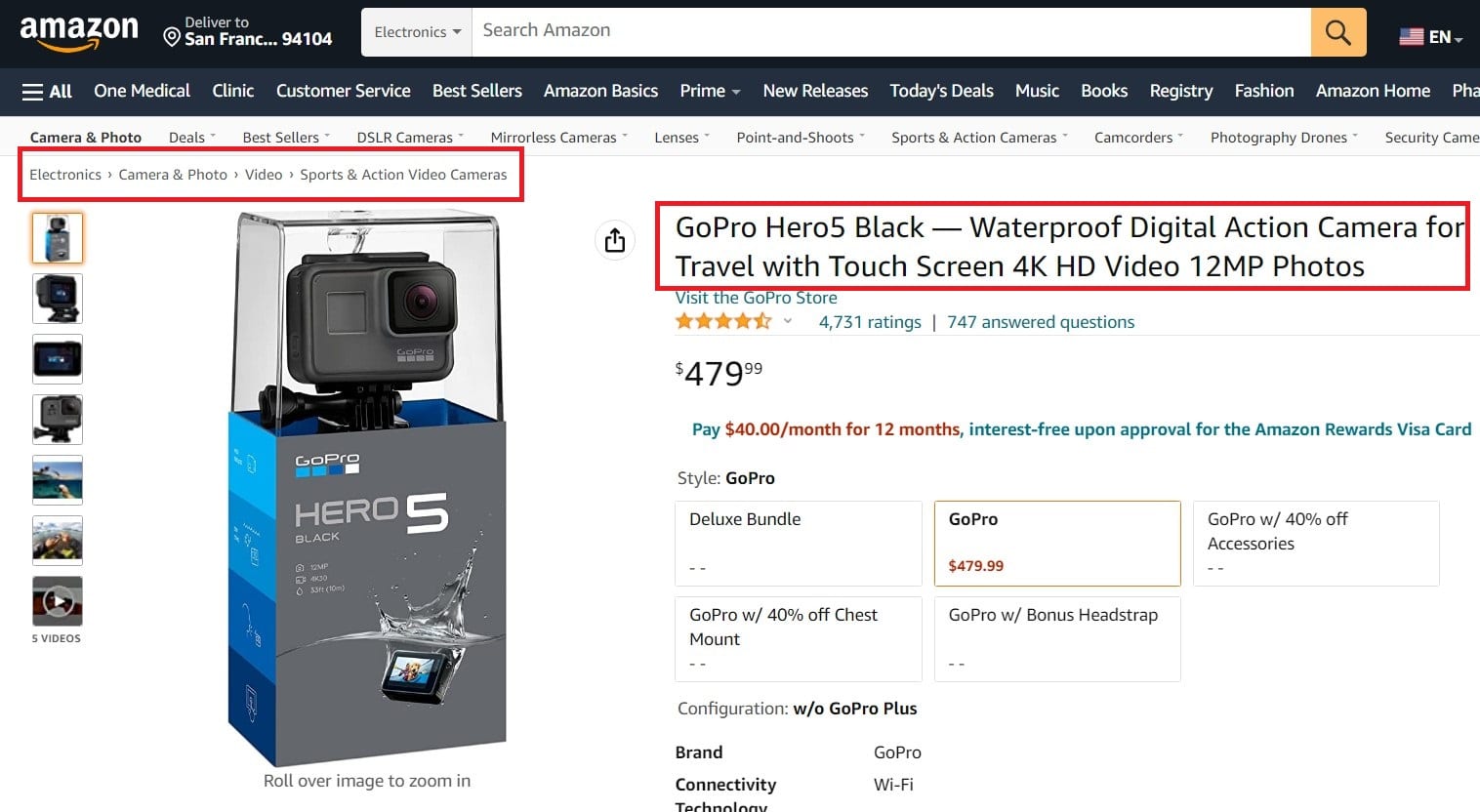

We find words like: “Electronics”, “Camera & Photo”, “Action Video Camera”, “Sports”, etc.
You may also want to check out the reviews for additional keywords.
Find keywords on Quora: This great community allows users to ask, and receive answers to, all types of questions. When there’s so much content, it’s always a good idea to search for keywords.
The way to do it is simple: just type your main keyword into the search engine. For our example, we’ll use “air jordan”.
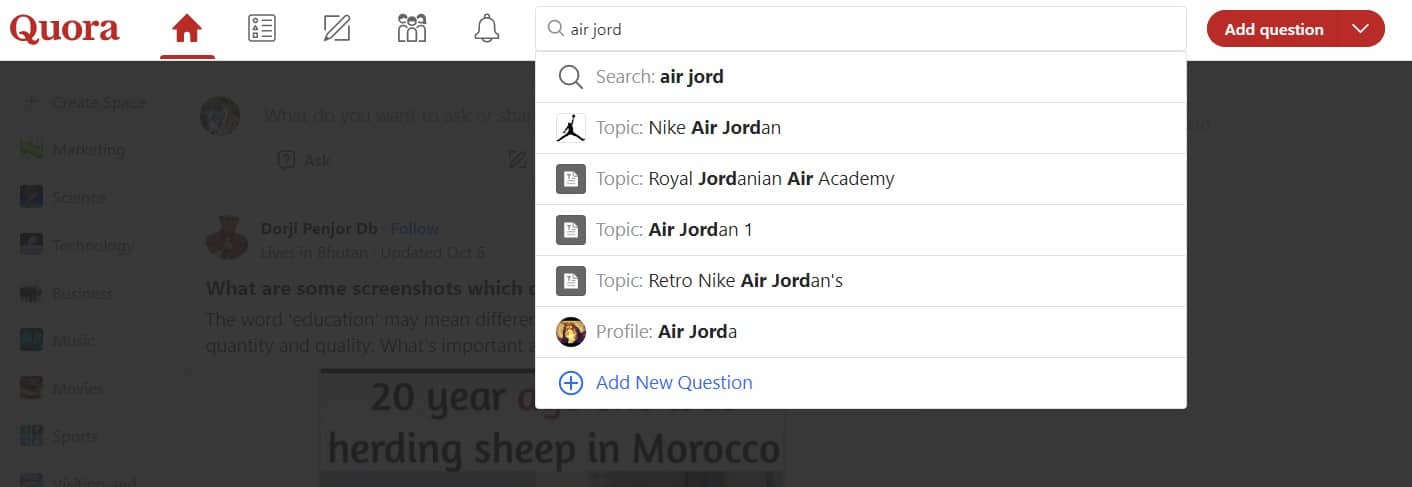
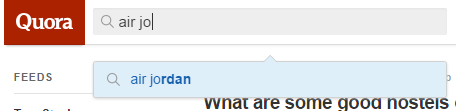

You’re now going to see a list of search results. Check out different questions related to your product – such as this one: “What are the best-selling Air Jordans?”. This is a long-tail keyword in its own right that you can use for your blog.
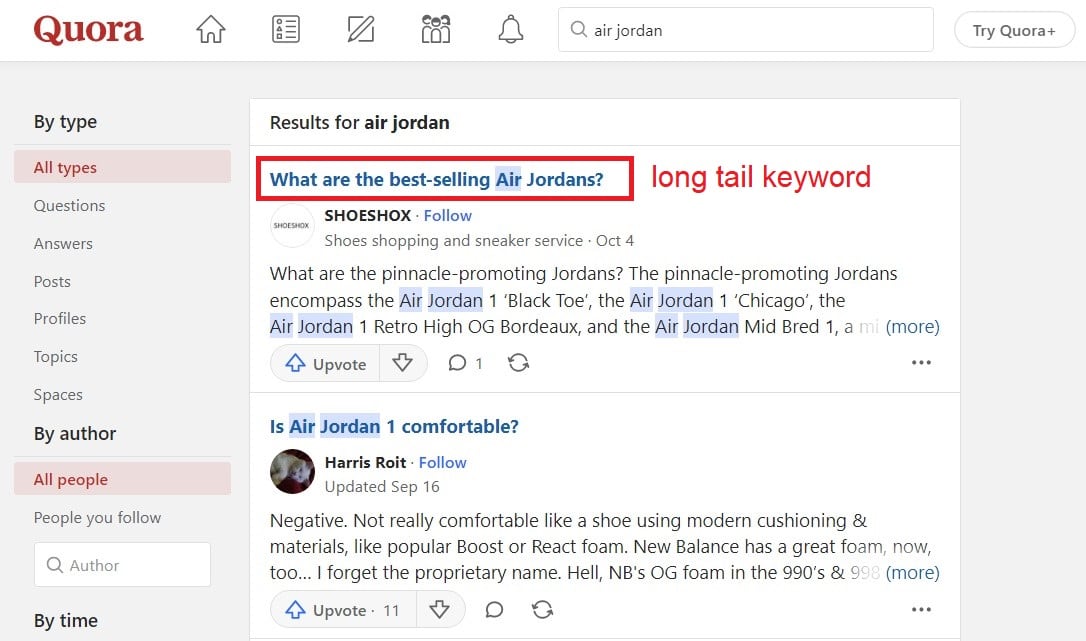
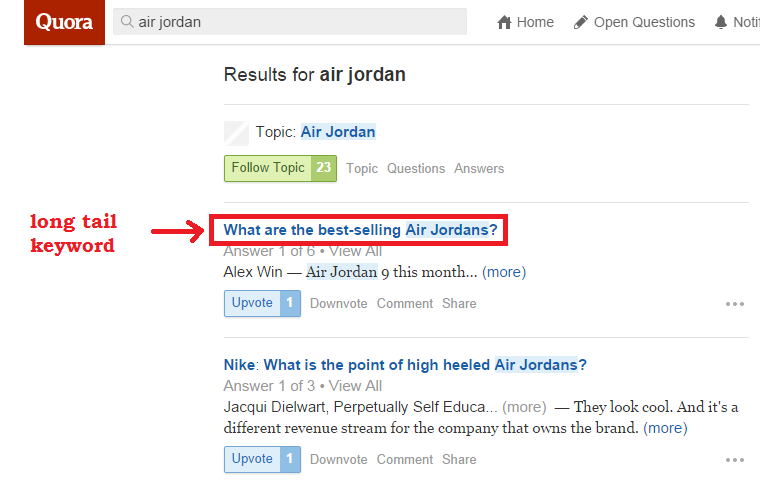

Inside the questions and answers, you can find additional keywords which you can use for your SEO strategy.
Find keywords with SEOquake: This is a great free tool that lets you analyze your competition and find out which keywords they’re using to rank in search engines.
Go to your competitor and his product page – in this example: Amazon.com and Microphone for iPhone and Smartphones
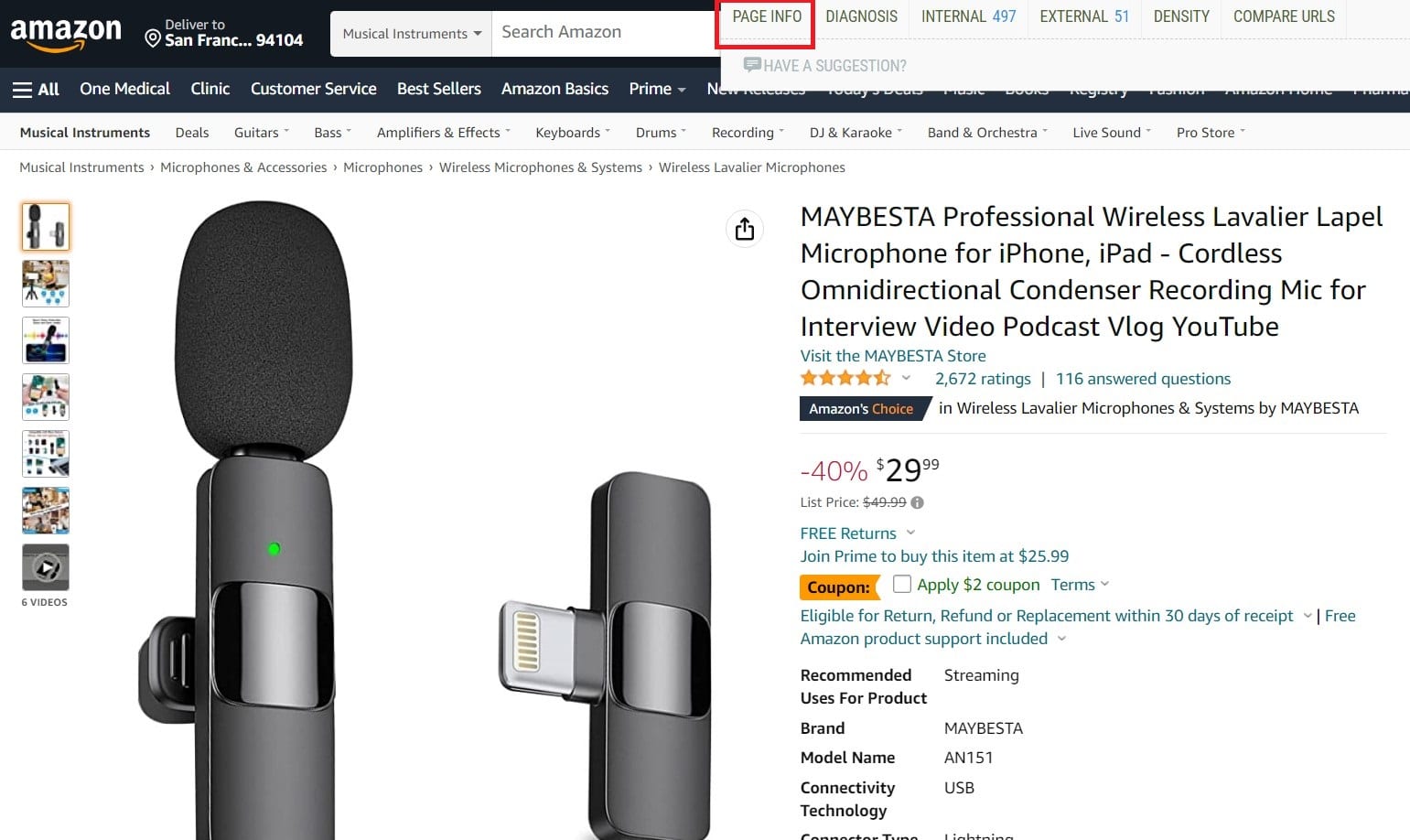
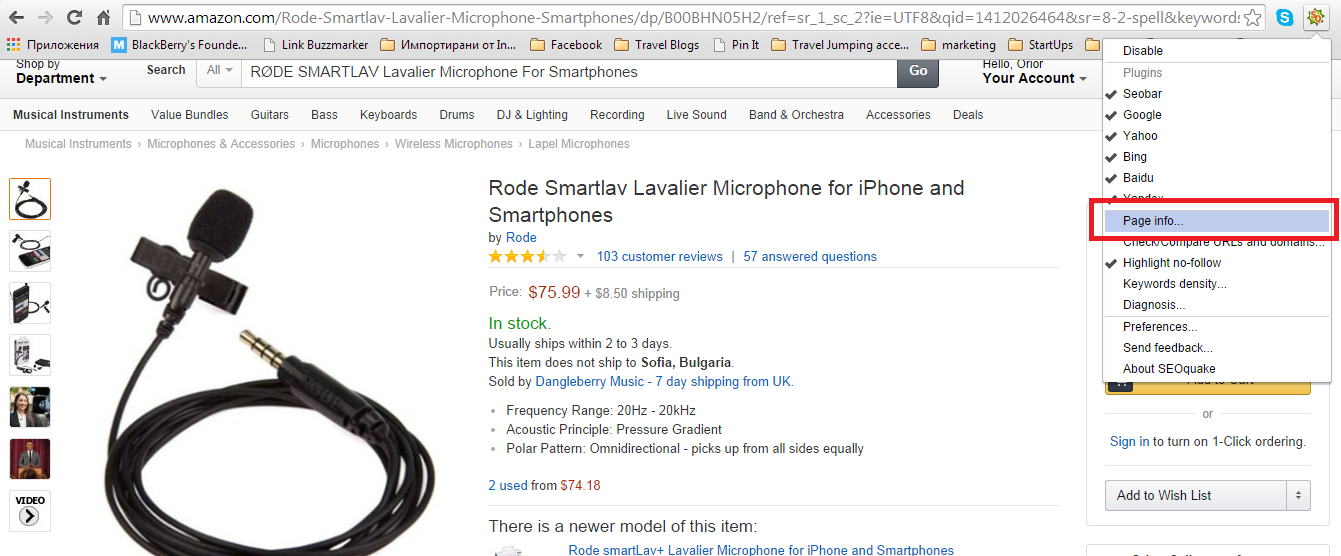

Click on your SEOquake bar and select “Page info”. The following information will be displayed:
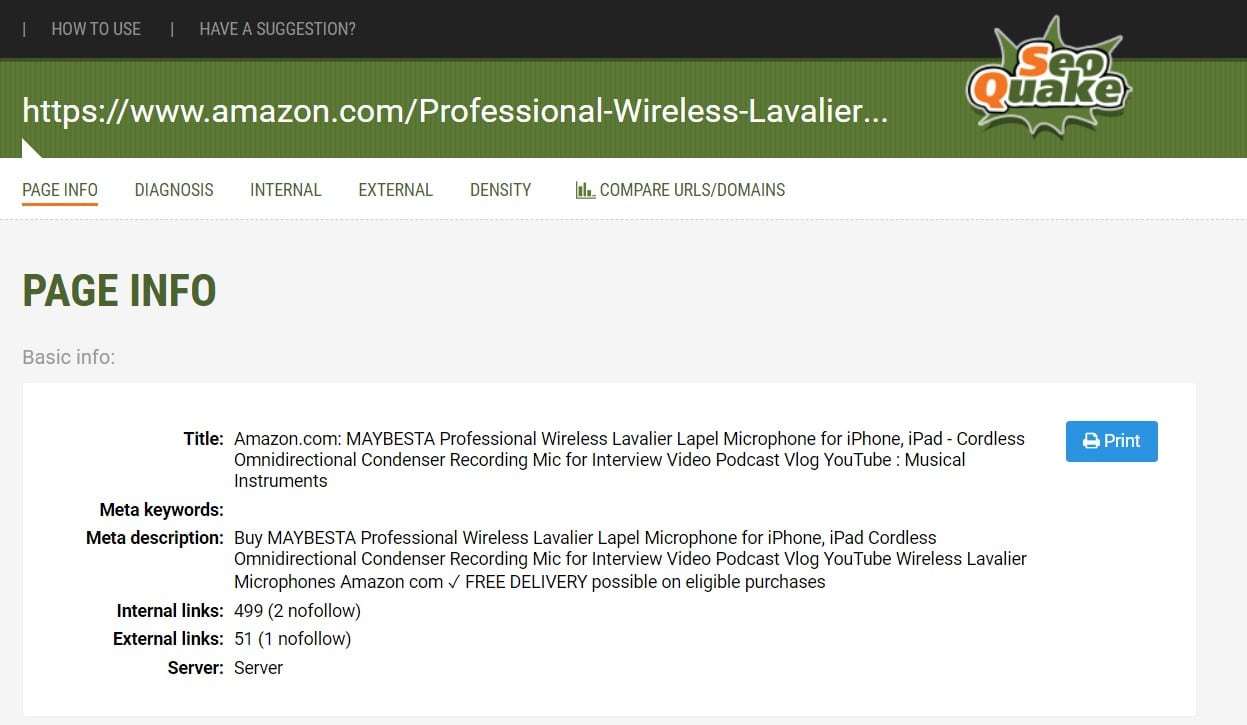
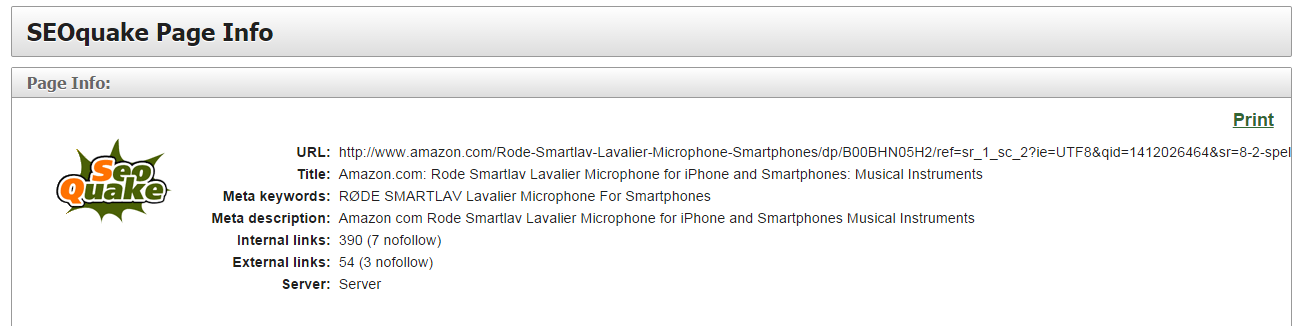

Now you can see the title, description, and meta-keywords of the page.
More Keyword Research Tools
In addition to the tools above, Ahrefs is a powerful SEO tool that provides insights into keyword rankings, backlinks, and organic search traffic. With Ahrefs, you can see what keywords your competitors are ranking for, track your own keyword rankings, and identify opportunities for new content.
SEMrush is another popular SEO tool that provides insights into keyword research, site audits, and backlink analysis. With SEMrush, you can identify new keyword opportunities, track your website’s search performance, and analyze your competitors’ SEO strategies. Moz also has Keyword Explorer which is a keyword research tool that provides insights into search volume, and keyword difficulty.
Expanding Further
In addition to the tools and methods discussed earlier, there are several other strategies you can use to expand your keyword ideas:
- Look for related keywords: Once you have a list of primary keywords, try to identify related keywords that you can target. For example, if your primary keyword is “running shoes”, related keywords could include “trail running shoes”, “marathon running shoes”, “lightweight running shoes”, and so on.
- Use keyword research tools: In addition to the tools mentioned earlier, there are several other keyword research tools available, such as Google Trends, Keyword Tool, and Wordtracker. These tools can provide additional insights into search volumes, related keywords, and competition levels.
- Analyze your competitors: Another strategy is to analyze the keywords that your competitors are targeting. You can use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to identify the keywords that your competitors are ranking for and use this information to inform your own keyword strategy.
- Use customer feedback: Finally, you can use customer feedback and reviews to identify potential keywords. Look for common themes or phrases in customer feedback and use these to identify potential new keywords.
By using a combination of these strategies, you can create a comprehensive list of relevant and high-traffic keywords to target in your SEO strategy.
Step 4: Refine your keywords
Now that you’ve gathered a big list of potential keywords, it’s time to trim the fat. Not every keyword is worth targeting , and going after the wrong ones can waste time and dilute your strategy.
This step is all about refining your list so you’re left with keywords that are relevant, high-converting, and realistic to rank for.
Remove all keywords that:
- Keywords unrelated to your products
- Keywords with extremely low search volume (no one’s searching for them)
- Super competitive keywords that big brands already dominate
- Vague terms with unclear intent
Instead, focus on words that:
- are related to your core business and products that you offer.
- have high search volume.
- have low competition.
- are long-tail and more specific.
Go to Google Trends, and see whether the search volume for the keyword is increasing and decreasing with time.
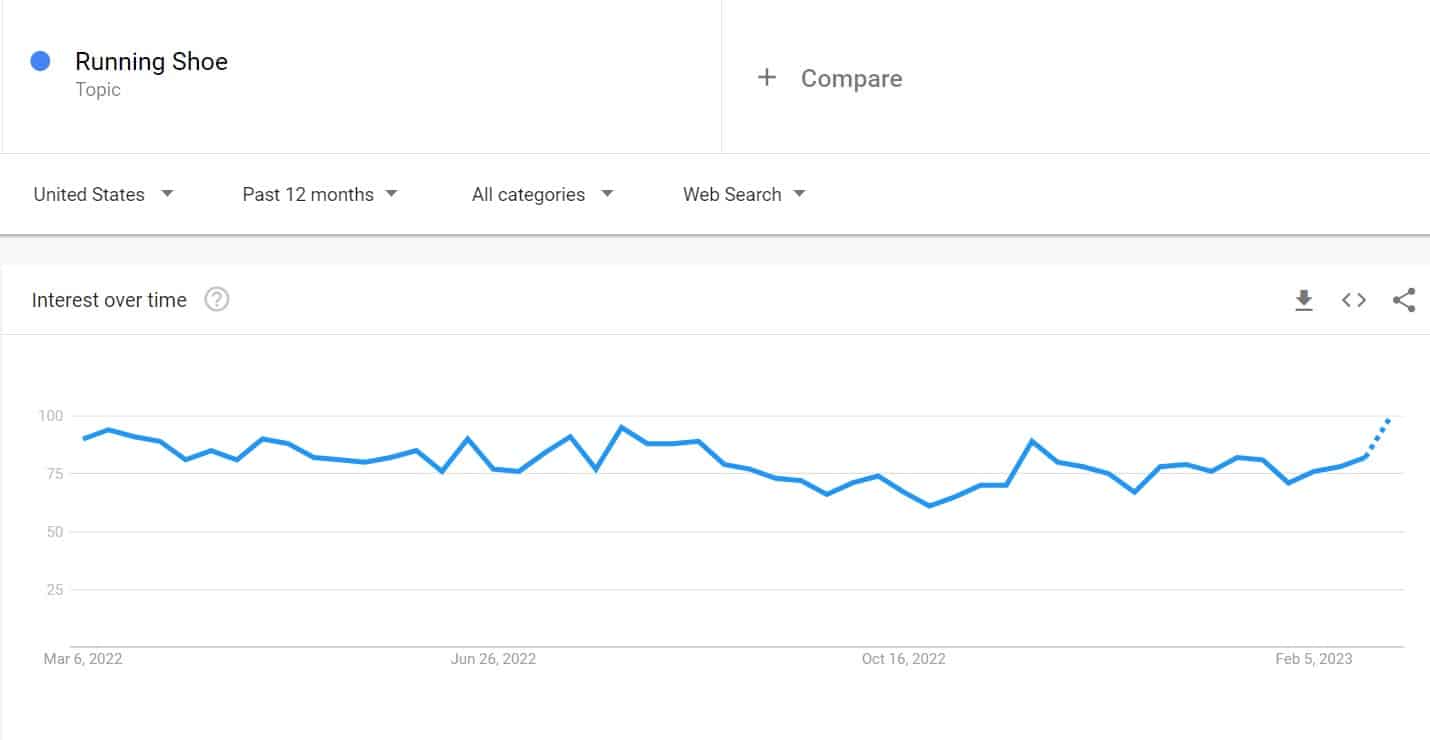

As you can see, the trend for Running shoes is definitely upward, so the market for these shoes won’t bottom out anytime soon.
If you’re unsure which keywords to keep, ask yourself, would someone searching for this be happy to land on one of my product pages or blog posts?
If the answer’s no, it’s probably not the right keyword for you.
Step 5: Build Your Keyword Strategy for Revenue, Not Just Traffic
Getting traffic is great, but traffic alone doesn’t pay the bills. For ecommerce sites, your keyword strategy should focus on one thing above all: conversions.
Some keywords bring in curious browsers. Others attract ready-to-buy customers. Your job is to tell the difference — and prioritize the ones that move the needle.
Here are five types of keywords, ranked by how likely they are to drive revenue:
1. Buy-now keywords
These include words like “buy,” “discount,” “coupon,” “deal,” or “free shipping.” People searching for these are ready to purchase. You want to target these terms on your product pages and collection pages.
2. Product keywords
These include specific brand names, product models, or phrases like “best wireless earbuds,” “affordable running shoes,” or “top 10 standing desks.” These searches often signal intent to buy — just not immediately.
3. Informational keywords
These might include questions like “how to choose a hiking backpack” or “what is the difference between OLED and QLED TVs.” They’re earlier in the buying journey, but still important — especially for blog content or guides.
4. Navigational keywords
These are brand-specific searches, like “Nike” or “Target return policy.” They usually come from people already familiar with a company. If your brand is well known, you’ll naturally rank for these.
5. Freebie or tire-kicker keywords
Searches like “free download” or “torrent” generally bring traffic that won’t convert. Avoid building content around these unless you have a very specific lead capture strategy.
Bottom line? Focus most of your efforts on buy-now and product keywords, and support them with informational content to build trust and bring in searchers earlier in the journey.
Using Competitive Analysis in Keyword Research
Another smart move: spy on your competitors.
By analyzing what keywords your top competitors rank for, you can uncover content gaps and opportunities for your own site. Tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or SpyFu make this easy.
Look for:
- Keywords they rank for that you don’t
- High-traffic blog posts or product categories
- Content formats they use to rank (videos, FAQs, long-form posts)
When you spot a keyword they’re doing well with — and you sell the same or better product — that’s your chance to create something stronger, more complete, and more helpful.
Understand User Intent Before You Hit Publish
One of the biggest SEO mistakes? Choosing keywords without thinking about why someone is searching.
User intent generally falls into three buckets:
- Informational – looking to learn
- Navigational – looking for a specific site
- Transactional – looking to buy
Make sure the content you create matches the searcher’s intent. If the keyword is “best indoor plants for low light,” the user expects a roundup — not a product page or a definition.
Aligning your content with intent increases the chances Google will rank it — and that visitors will take the action you want.
Pro Tips to Keep Your Keyword Strategy Strong
Once you’ve built your strategy and started implementing it, don’t stop there. Keyword research is never really “done.”
Here’s how to keep improving:
- Monitor rankings regularly with tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush
- Use Google Analytics to see which pages drive traffic and which ones convert
- Update old content to reflect new keyword opportunities or shifting trends
- Watch competitors to see if new keywords or content strategies are emerging
- Keep an eye on search trends with tools like Google Trends or Exploding Topics
SEO is an ongoing game — but that’s what makes it so powerful. The more consistently you refine your keywords and content, the more organic visibility you’ll build over time.
Conclusion: Your Ecommerce SEO Starts with Keywords
If you’ve stuck with me this far, you already get it: Ecommerce keyword research isn’t just about chasing numbers and traffic. It’s about truly understanding your audience, meeting them where they are, and building a strategy that turns casual browsers into loyal customers.
The ecommerce businesses that win at SEO aren’t just the ones with the most visitors – they’re the ones targeting actual buyers. And it all starts with a thoughtful, strategic approach to keywords.
Put in the work now, and you’ll enjoy the rewards: steady traffic, stronger rankings, and a store that grows even while you sleep.

Comments